Quick Summary :- In this modern world, we have lot of technologies available in the market which are offering effective development solutions. But then a question arises is the particular technology perfect for my development requirement. This becomes difficult for businesses to differentiate between various Technologies and pick out the best one. So to resolve the confusion, we have brought the extensive comparison between two vital technologies namely React & Angular.
Comparison between React and Angular is a famous topic in the world of technology. Both of these are modern and greatly acknowledged JavaScript (JS) technologies used to build interactive single-page applications (SPAs). Today, we will compare React vs Angular.
Both Angular and React are used by many industries in the USA, the UK, Canada, France, Germany, and Australia, among other countries.
In this article, you will go through many insights and information to decide which one of these is suitable for your requirements. You will understand how both use different philosophies to tackle similar front-end issues.
Overview, Features & History: React Vs. Angular
What is React?
Meta created the JS library React that helps you in developing UI components. It makes the process of creating interactive user interfaces better and simpler.
When developers use React, it makes the code easier to understand and launch. React JS framework utilizes server-side rendering to offer an adaptable and performance-oriented solution.
Features of React
- Lets you use third-party libraries
- Saves time
- Simple and composable
- Quicker development
- Fast performance and better user experience
- Code stability with one-directional data binding
- Has React components
For Detailed Features of React Visit: https://www.esparkinfo.com/software-development/technologies/reactjs/features
History of React
- Jordan Walke, a software engineer from Facebook, created React in 2011.
- Released as open-source in May 2013.
- v16.0.0 – September 26, 2017 : Introduced fragments, error boundaries, portals, support for custom DOM attributes, improved server‑side rendering, and reduced file size. (Source – React )
- v18.0.0 – March 29, 2022 : Introduced Concurrent React with automatic batching, new Suspense features, transitions, and streaming server‑side rendering with Suspense support. (Source – ReactGitClear )
- v18.1.0 – April 26, 2022 : Delivered various bug fixes and performance improvements across React DOM and the core reconciler. (Source – Wikipedia )
- v18.2.0 – June 14, 2022 : Included additional fixes, optimizations, and stability enhancements for concurrent features and SSR. (Source – Wikipedia )
- v18.3.0 – April 25, 2024 : Added deprecation warnings for features slated for removal in React 19 and minor enhancements. (Source – GitHub )
- v18.3.1 – April 26, 2024 : Patch release fixing minor bugs and exporting act from the main React package for improved testing workflows. (Source – GitHub )
- v19.0.0 – December 5, 2024 : Introduced Actions, new hooks (useActionState, useFormStatus, useOptimistic), the experimental use API, stable Server Components with Server Actions, and enhanced hydration diffs (Source – GitHubWikipedia )
- v19.1.0 – March 28, 2025 : Offered performance tweaks, minor fixes, and preparatory changes ahead of the React 20 cycle. (Source – GitHubnpmjs.com )
What is Angular?
Angular is a structural framework used in creating dynamic web applications. It lets the developers use HTML as a template language and lets HTML syntax express the application’s components concisely and clearly.
Also, it assists the MVC programming structure. It is a fully-featured JS framework that supports creating dynamic, single-page web applications.
Features of Angular
- Built-in support for HTTP, AJAX, and Observables
- Great community support
- Consistent with technology
- Neat and crisp coding
- Typescript offers efficiency
- Upgraded support for error handling
- Seamless updates using Angular CLI
- Forms and validation
- Shadow DOM/Local CSS
- UI and Business Logic Separation
For Detailed Features of Angular Visit: https://www.esparkinfo.com/software-development/technologies/angular/advantages
History of Angular
- Angular was released by Google in 2010.
- Angular 2.0 was released in September 2016.
- Angular 4 was released on March 23, 2017.
- Angular 5 was released on November 1, 2017.
- Angular 6 was released on May 4, 2018.
- Angular 7 was released on October 18, 2018.
- Angular 8 was released on May 28, 2019.
- Angular 9 was released on February 6, 2020.
- Angular 10 was released on June 24, 2020.
- Angular 11 was released on November 11, 2020.
- Angular 12 was released on May 12, 2021.
- Angular 13 was released on November 4, 2021.
- Angular 14 was released on June 2, 2021.
- Angular 15 was released on November 16, 2022.
- Angular 16 was released on 03 May 2023
- Angular 17 was released on November 8, 2023
- Angular 18 – Released May 22, 2024 ( Source – Wikipedia )
- Angular 19 – Released November 19, 2024 ( Source – Wikipedia )
- Angular 20.0.0-next.5 (pre‑release) – Published April 2, 2025 ( Source – GitClear )
Benefits and Drawbacks of React and Angular
React: Benefits and Drawbacks
React Benefits: Why Use React?
- Its simple design makes it easier to learn.
- The HTML-like syntax provides templating and greatly detailed documentation.
- Developers can effectively utilize more time in writing modern JS, and invest less time in bothering about the framework-specific code.
- A strong framework for content-focused applications due to its advanced support for server-side rendering.
- Developers can migrate between versions.
- Facebook provides a ‘codemod’ feature to automate a large part of the process.
- Developers can apply the skills learned in React to Native development.
- When collated with ES6/7, React becomes ideal for handling heavy loads with relative ease.
Drawbacks of React
- The complicated configuration is necessary when integrating React in a traditional framework like Rail.
- Developers who use React should have a thorough knowledge of the integration of user interfaces into the MVC framework.
Angular: Benefits and Drawbacks
Angular Benefits: Why Use Angular?
- Offers neat code development
- Greater performance
- Material Design-like interface
- Handles routine brilliantly moves one view from another easy
- Seamless updates using Angular CLI
Drawbacks of Angular
- Beginners could get confused with Angular’s features
- Lack of a clear manual and detailed, all-inclusive documentation
- Steep learning curve
- Scopes are difficult to debug limited routing
- Sometimes gets slow with pages embedding interactive elements
- Difficult third-party integration
- Developers face hurdles when switching from the older versions to the newer versions
Angular vs. React: A Quick Comparison Table
| Parameter | React | Angular |
|---|---|---|
| Type | JavaScript Library | Complete Framework |
| Use Of Libraries | Can Be Packaged With Other Libraries | Complete Solution |
| Learning Curve | Small | Big |
| Community Support | Vast & Active | Large & Well-Supported |
| Installation Time | High | Low |
| Best Feature | Allows you to choose tools, architecture, and libraries | Limited freedom & flexibility |
| Data Binding | One-Way | Two-Way |
| Testing & Debugging | Require Set Of Tools | One Single Tool |
| Documentation | Faster | Slower |
| Updates | Simple | Complex |
| Ideal For | Native-Rendered Apps | Large-Scale Apps |
| Model | Virtual DOM | MVC |
| Written In | JavaScript | Typescript |
| Template | JSX + J5 (ES5/ES6) | HTML + Typescript |
| GitHub Stars | ~235K+ (as of Q1 2025) | ~97.5K+ (as of Q1 2025) |
Angular vs React: Detailed Benchmark Comparision by Our Developers
Universality: React Vs Angular
React
It is a framework implemented in both, web app development and mobile app development. However, for mobile development, it is required to be integrated with Cordova. In addition, for mobile development, there is an additional framework – React Native. Developers use React for building single-page and multiple-page web applications.
Angular
It is apt for both web and mobile development. In mobile development, Ionic handles a large portion of the work. Like React, Angular also has an extra mobile development framework. The equivalent of React Native is NativeScript.
Angular can also be utilized for the creation of both, single- and multiple-page web apps.
So, in the race of Angular vs React for universality, both are on level terms.
Self Sufficiency: React Vs Angular
React
For UI development the React framework is used, hence, apps written with React require extra libraries. Redux, React Router, or Helmet optimize the processes of state management, routing, and interaction with the API.
Functions such as data binding, component-based routing, project generation, form validation, or dependency injection need the installation of supplemental modules or libraries.
Angular
It is a complete framework for custom software development that generally does not need the installation of extra libraries.
All the functions mentioned: data binding, component-based routing, project generation, form validation, or dependency injection, could be implemented within the Angular package.
Learning Curve: React Vs Angular
React
This framework is easy to understand if you are already well aware of JavaScript. React is minimalistic, it has no dependency injection, no classic frameworks, and no excessively complex features.
However, hire a React developer who spends some time learning how to set up a project as there is no predefined project structure.
For example, the Redux library is implemented in many React applications for state management. The regular framework updates also need extra effort. Developers need to learn the best practices that will help them in many things.
Angular
Angular is a massive library, and studying the important concepts will require more time than React. It is more complicated to comprehend, component management is complex, and it comes with plenty of needless syntaxes.
However, TypeScript is quite similar to JavaScript but that also requires time to learn. Developers need to strive as the framework is regularly updated.
Community: React Vs Angular
React
One of the well-acknowledged JS frameworks, React has great community support and development.
Developers need to continuously learn while working with React as the framework gets regular updates. Though the community puts its efforts into maintaining the latest documentation, sometimes there could be a miss.
However, if there is an issue, it usually gets answered by community support on thematic forums.
Angular
Compared to React, Angular is less popular and many developers doubt it, partly because Angular 1.0 was unpopular.
As the framework needed developers to spend a good amount of time learning, it was considered excessively complex. However, Google has created this framework so it makes Angular’s reputation stronger.
Google offers continuous updates and long-term support for the framework. The updates being so quick can make it difficult to maintain the documentation.
So, in the race of Angular vs React for the community, Angular is slightly ahead.
Performance Comparison: React’s Virtual DOM vs Angular’s update
React
The introduction of the virtual DOM has played a major role in enhancing React’s performance. The load on the browser decreases as all virtual DOM trees are lightweight and created on the server.
As the data-binding process is unidirectional, watchers are not assigned to bindings as in the case of Angular. Respectively, no extra workload gets created.
Angular
Angular performance is not satisfactory in the case of dynamic and complicated web apps. Bidirectional data-binding negatively impacts Angular apps’ performance.
For every binding, there is a watcher to track changes, and every loop continues till all the watchers and associated values are checked.
Due to this, the number of watchers increases as the number of bindings increase, making the process convoluted.
However, the latest Angular’s update betters its performance and makes it compete with React. The size of an Angular application is a little smaller than the size of a React app.
So, in the battle of React vs Angular Performance, Angular wins here.
Language: React Vs Angular
React
It is based on JS ES6+ merged with JSX script. JSX is an extension for syntax and it makes a JS code similar to that written in HTML.
Due to this, developers easily find typos and the code becomes simpler to understand. When the JSX code needs to be compiled in a browser, React is supplemented with Babel, a code translation tool.
Angular
It can use JS or TypeScript, a superset of JS particularly created for bigger projects. TypeScript is briefer than JS. Developers can effortlessly find typos and smoothly go through the code. This makes the code refactoring process also easier and quicker.
App Structure: Angular Vs React
React
With React’s structure, the developers have the freedom of choice. For React, there is not just one right structure.
Although, the prerequisite to designing the app structure right at the start of the project could make it difficult and take more time to begin the process.
React provides only the View layer and with the usage of other libraries, Model and Controller are included.
A React app’s architecture is component-based. React components form the code that is rendered with the React DOM library and directed in two ways: functional (with a function that returns JSX) and class-based (with ES6 classes).
Functional:
function Hello(props){
return <div>Hello {props.name}</div>
}
Class-based:
class Hello extends React.Component {
render() {
return <h1>Hello, {this.props.name}</h1>;
}
Angular
For experienced developers, the structure of Angular is apt as it is predetermined and complex. It is based on three layers: Model, Controller, and View. An object accountable for the Model is initialized by the Controller and is shown with the View.
The app code has various Angular components, every component is written in four different files: an HTML file to define the View, a TypeScript to implement the component, a CSS file to define the stylistic features and a particular file for testing purposes.
The app directive, where the links to these files are written, displays the app’s structural logic. Angular components can be reused.
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'my-app',
templateUrl: './app.component',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent { }
UI Components: ReactJS Vs AngularJS
React
The React community has created the UI tools for React. Developers can access many free and paid UI components on the React portal.
If developers want to use Material Design components in React, they would have to install an extra library – Material-UI library and dependencies.
Angular
It comes with a built-in Material toolset that provides numerous pre-built Material Design components. Plan to hire Angularjs Developers as they possess expertise in working with various buttons, indicators, pop-ups, layouts, and form controls. This makes the UI configuration quicker and simpler.
So, in the race of Angular vs React, Angular has more options in terms of UI.
Directives: Angular Vs React
React
In React, templates and logic are described at the end of the component. For a reader, it becomes easier to understand the meaning of the code even if they do not know the syntax.
Angular
In Angular, every template comes with an attribute, which is a directive on how to set the object. The readers need to be experienced and aware of this technology as Angular directives are complex and advanced. So, both Angular or React have different perceptions.
State Management: React Vs. Angular
React
In React, every component has its state. To maintain the state of the full application or a specific part of it, a React developer can build special components.
The drawback is that the global state has to be stored in numerous parts of the app with data being manually passed around different component tree levels.
class Clock extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {date: new Date()};
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Hello world!</h1>
<h2>Now is {this.state.date.toLocaleTimeString()}.</h2>
</div>
);
}
}
Redux, a special state management library, can solve this issue. MobX is another state management library that can be helpful.
Angular
In Angular, the component data is stored in component properties. Through the children components, parent components pass the data.
In some parts, state changes can be recognized and recalculated. In a large app, it can lead to a multi-directional tree series of updates that are hard to track.
With the assistance of state management libraries like NgRx or RxJS, the above-mentioned features could become better as the state management libraries ensure a unidirectional data flow.
export class HeroListComponent implements OnInit {
heroes: Hero[];
selectedHero: Hero;
constructor(private service: HeroService) { }
ngOnInit() {
this.heroes = this.service.getHeroes();
}
selectHero(hero: Hero) { this.selectedHero = hero; }
}
Dependency Injection: React Vs Angular
React
React does not completely follow the concept of functional programming and data immutability, hence, it does not completely support dependency injection. In place of that, it has a global state for all components.
Angular
Angular supports dependency injection, which gives it an edge over React. It allows having different life cycles for different stores.
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { HEROES } from './mock-heroes';
@Injectable({
// we declare that this service should be created
// by the root application injector.
providedIn: 'root',
})
export class HeroService {
getHeroes() { return HEROES; }
}
Data Binding: React Vs Angular
React
Data binding means the data synchronization process between Model and View. React is supplemented with Redux, which lets the developers work with immutable data and makes the data move unidirectionally. Unidirectional binding is anticipated, this eases up the debugging process.
Angular
It operates with bidirectional data-binding and mutable data. This makes it simpler for the developers to operate with bidirectional data binding instead of working with the unidirectional approach.
Bidirectional data-binding has a negative impact on performance as Angular by itself creates a watcher for every binding.
The ways of data-binding in Angular:
{{expression}} Interpolation
[target]="expression" Property
bind-target="expression" Attribute
(target)="statement" Event
on-target="statement" Event
[(target)]="expression" Two-way
bindon-target="expression" Two-way
So, in the terms of React vs Angular, both have different perspectives.
Change Rendering: React Vs. Angular
React
It utilises a virtual Document Object Model (DOM), which allows simple implementation of minor data changes in one element without updating the structure of the entire tree.
The framework builds an in-memory cache of data structure, calculates the changes, and effectively updates the DOP shown in the browser.
The React team is putting continuous efforts in improving Fiber, a mechanism that focuses on boosting the productivity of change rendering.
Angular
It utilises a real DOM. It updates the complete tree structure even when the changes have appeared in just one element. Compared to the virtual DOM, the real DOM is slower and less effective.
To overcome this disadvantage, Angular uses change detection to find components that need to be adjusted. Thus, the real DOM gives similar performance as the virtual DOM on React.
So, for DOM, the battle of React vs Angular goes to React for speed.
Tools: React Vs. Angular
React
Various code editors support React. For example, the code in React can be edited with Sublime Text, Visual Studio, and Atom. If the developer needs to bootstrap a project, they can use the Create React App (CLI) tool. With the Next.js framework, the server-side rendering is finished.
To verify the complete app written in React, multiple tools are required. For example, Enzyme is used for component testing, Jest for testing JS code, and React-unit for unit testing, among others.
A browser extension, React Dev Tools, can be used to debug the app in the development phase.React 360, a library can be used for creating AR and VR applications.
Angular
Just like React, Angular also has numerous code editing tools such as Aptana, Sublime Text, and Visual Studio. With Angular CLI, a project can be quickly set up. With the assistance of Angular Universal, server-side rendering could be finished.
A single tool can completely test an app written with Angular. Jasmine, Protractor, and Karma are used for end-to-end testing. A browser extension, Augury, debugs the app in the development phase.
So, knowing about ReactJS vs AngularJS in terms of tools is essential.
Maturity: Angular Vs. React
React
Facebook created React and also maintains it. Facebook uses React in its own products, which include Instagram and WhatsApp. React has been in the business for almost seven years. It is one of the most accepted projects on GitHub, with almost 150k stars.
Angular
Maintained by Google, Angular has been around for almost 10 years. It is used in more than 600 applications in Google such as Google Analytics, Google Cloud Platform, Google Express, and Firebase Console among others.
So, in terms of maturity, Angular wins the ReactJS vs Angular race.
Ecosystem: React Vs Angular
React
The well-known tools and libraries associated with React are:
Create React App, React Native, Material UI, Next.js, Gatsby, React 360, and React Developer Tools
Angular
The well-known tools and libraries associated with Angular are:
Angular CLI, Ionic Framework, Angular Material. Angular Universal, and Augury
So, knowing this aspect is critical for a feature-based comparison of React JS vs Angular.
Componentization: React Vs. Angular
React
React provides a straightforward method of creating component trees. The library already has functional programming in which the component definitions are declarative.
React codes are readable and logically structured. They do not require the developers to write code in a particular manner.
Angular
It has an exceptionally rigid and complicated structure as it is based on three layers: Model, View, and Controller.
With Angular, the developers need to decide the app’s code in various files. This way, they can reuse templates or the components in various parts of the application.
Angular vs React JS has been an ongoing battle and this adds another chapter to that.
Popularity: React Vs. Angular
Both technologies have their own community and a fair share of popularity. According to Google Trends, Reach is searched more than Angular. On a different note, Angular has many ready-made solutions which makes it equally popular.
Angular is a whole framework while ReactJS is an exhaustive library. Both are used extensively for front-end development. But, there is a vast difference between the popularity of Angular and ReactJS among developers and businesses.
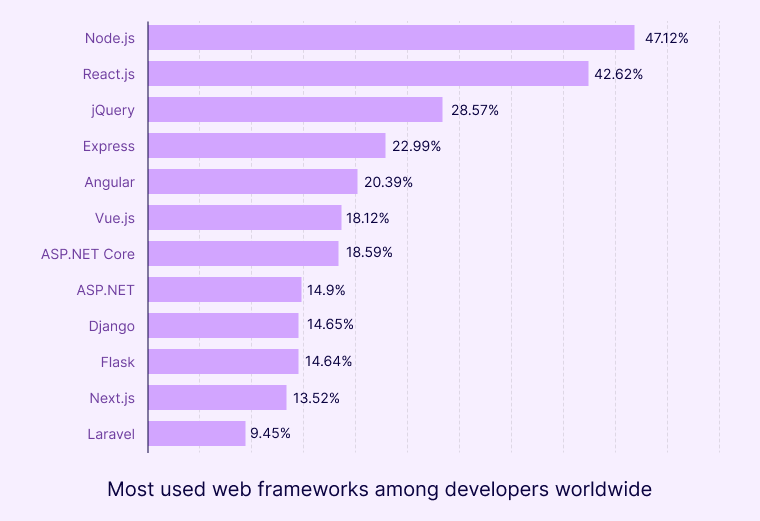
According to Statista, ReactJS stands at the 2nd rank with double the users of Angular, as the most used web framework among developers in 2022.
Launched after Angular, React has gathered a wider community and favor due to its incredible usability and flexibility to be combined with other techs & frameworks. Thus, producing a more dynamic, real-time, & wide range of digital solutions. While, Angular has retained its position due to its ready-made, sturdy, & reliable solutions. However, with time and advancement, both are evolving drastically to meet the changing demands.
Architecture: React Vs. Angular
React
It has component-based architecture, meaning it is connected, reusable, and has modular components. React architecture uses JS for development.
Angular
It also has component-based architecture. The difference between Angular and React is in their tech stack. Angular uses TypeScript for web development which is more compact and has no errors. So, this is the key Difference Between React and Angular.
Development Speed: Angular Vs. React
React
With React, the development speed and productivity gets impacted as third-party libraries are involved. The developers need to decide the right architecture when choosing the tools.
Also, the toolkit of React mobile apps is different in different projects. This means when new developers start handling the app updates, they need to invest more time and effort.
Angular
It offers a great development experience. This happens because CLI enables the creation of a workspace and designs functioning apps smoothly.
It also creates components and services with one-line commands, built-in processes to solve detailed issues, and cleans code, a feature of TypeScript.
Flexibility: Angular Vs. React
React
When developers use React, they have the freedom to select the tools, libraries, and architecture for app development. With this freedom, they can build a highly-customised app only with the features and tech stack they need.
Angular
It comes with restricted freedom and flexibility. Developers have limitations in using Angular components in frameworks.
DOM: Angular Vs. React
React
It uses virtual DOM. Due to this, developers can track and make changes and this would not impact other parts of the tree. Virtual DOM is also faster.
Angular
It uses real DOM. Due to this, even if the developers make a single change, the whole tree data structure gets updated.
Mobile App Development: React Native vs Angular with Ionic/NativeScript
React
It offers a real native UI experience that empowers the developers to make their components and bind them to native code written in Java, Kotlin, and Objective-C.
Angular
It offers an Ionic framework for mobile development. It comes with a Cordova container and an appealing UI component library. When the developed application is viewed on any device, it seems like a web inside a native web app container.
Testing: Angular Vs. React
React
In React, a group of tools is needed to perform different types of testing. For example, Jest is required for code testing, Enzyme and Unexpected-React are required for component testing.
Skin-deep is required for Render testing utils, and React-unit for unit testing, among others. Due to this, developers need to spend more time and effort into the testing process.
Angular
For testing and debugging a full project in Angular, individual tools like Jasmine, Protractor, and Karma are required. A single tool saves developers’ time and energy spent on testing.
Ease Of Update: Angular Vs. React
React
Developers get the benefit of effortlessly transitioning between two versions. The front-end development library depends on the external libraries, this makes updating and migrating to the third-party components feasible.
The developers need to continuously check if the already in place third-party libraries are compatible with the latest versions of the JS framework or not. This entire process consumes time.
Angular
Its updated CLI consists of commands like ng_update that makes the process of upgrading the app to the latest Angular version possible. As a large part of the updating process is automated, the Angular app development becomes easier.
So, in the battle of Angular JS vs React JS, angular wins the race here.
Documentation: Angular Vs. React
React
The React framework gets many regular updates but the information from the earlier versions is still helpful and holds value.
Angular
The Angular framework’s documentation is lagging due to its continuous development process. Most of the documentation and tutorials are still AngularJS, it does not hold value for developers in present.
Templates: Angular Vs. React
React
It uses JSX and an XML-language that lets the developers write markup directly in their JS code. JSX is very helpful in development as everything is in one place, and code completion and compile-times checks work better. In React, developers need to only know JS.
Angular
It uses templates that are enhanced HTML with Angular directives (“ng-if” or “ng-for”).
Routing: Angular Vs. React
Component-based routing lets components handle their sub-routes rather than having one nig global router configuration. This approach is in react-router in version 4.
Form Validation: Angular Vs. React
Form validations are an important and commonly used feature. Both Angular and React support this feature with all the facilities being included.
Links and Imperative Navigation: Angular Vs. React
React
It has a more straightforward composability.
import * as style from './app.css'
// …
<h1>Shoutboard Application</h1>
<div>
<NavLink to='/home' activeClassName={style.active}>Home</NavLink>
<NavLink to='/posts' activeClassName={style.active}>Posts</NavLink>
</div>
<div>
{this.props.children}
</div>
React Router can also set the class of active link with activeClassName.
Here, developers cannot give the class name directly, because it’s been made unique by CSS modules compiler, and they need to use the style helper
Inside an <App> element, the react router uses the <Switch> element. As the <Switch> element just wraps and mounts the current route, it means that sub-routes of the current components are just this.props.children. So that’s composable too.
Angular
It is more intuitive.
<h1> Shoutboard Application </h1> <nav> <a routerLink="/home" routerLinkActive="active">Home</a> <a routerLink="/posts" routerLinkActive="active">Posts</a> </nav> <router-outlet></router-outlet>
Angular Router automatically finds the active routerLink, and places the right routerLinkActive class on it, so that it can be styled.
The router uses the special <router-outlet> element to render what the present path states. It’s possible to have many <router-outlet>s, as developers get more involved in the application’s sub-components.
@Injectable()
export class FormService {
constructor(private router: Router) { }
goBack() {
this.router.navigate(['/posts'])
}
}
The router module can be injected into any service. After that, the private declaration stores it on the instance without the need for an explicit assignment.
Famous Brands Using React and Angular
Famous Brands Using React
- Airbnb
- Uber
- Netflix
- Dropbox
Famous Brands Using Angular
- General Motors
- HBO
- Upwork
- Nike
- Forbes
- Sony
When to use React or Angular?
When to Use React?
- Your team members are proficient in HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
- Your app needs to be highly customised.
- You need a plethora of components with different and often variable states in the development process. For example, dynamic inputs, buttons enabled/disabled, a user’s login and access permissions, and active/inactive navigation items, among others.
- As the app project develops, the components need to be shared across multiple applications.
- You want to invest time in pre-development preparation.
When to Use Angular?
- Your team has a thorough understanding of Java, C#, and older versions of Angular.
- App complexity is between low and medium levels.
- You admire ready-to-use solutions and require more productivity.
- You are in favor of Bundle Budgets in the CLI option. It notifies the developers when the app’s bundle size surpasses the re-decided app bundle size. This helps you maintain the app size.
- You are looking for a large-scale feature-rich application.
Read also: Why Choose AngularJS For Web Development Project?
What Is the Future of React and Angular?
These two frameworks are highly admired by developers and have their own strengths and weaknesses. Is React Better Than Angular – this is also a question that needs to be answered.
React is coming up with great changes regularly. These changes are giving more power to the React developers to easily give feedback on new features, experimental APIs, and JS syntax developments. Angular is growing in terms of the usage rate.
Both frameworks, React and Angular, come up with regular updates to stay the most relevant to their loyal community.
The framework that will suit your requirements the best will depend on your app’s requirements, flexibility, complexity, and the proficiency of the team working on the project.
Conclusion: Making the Informed Choice for Your Project
React and Angular remain top contenders in the front-end world, each with solid backing from major tech companies and active developer communities. The main difference? React gives you a flexible UI toolkit that you’ll likely need to supplement with other libraries, while Angular hands you a complete package with all the essentials built right in.
These technologies handle things differently when it comes to performance, data flow, programming approach, and learning difficulty. I’ve found React works beautifully for dynamic interfaces and smaller applications, whereas Angular really shines when building larger enterprise systems with complex requirements.
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer here. Your best bet depends on what your specific project needs, how much it might grow, what your development team already knows, and how quickly you need to launch.
With 15+ years of building software, our teams at eSparkBiz have deep expertise in both React and Angular development. We’re happy to help you determine which technology makes the most sense for your particular business goals.
Ready to build your next cutting-edge web application? Partner with experts who understand how to harness the power of both React and Angular.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the Core differences between Angular vs. React?
Angular.js = Full Framework (TypeScript, MVC, built-in tools) and on the other hand React.js = UI Library (JavaScript/JSX, flexible, needs extra tools).
Which is faster framework?
Often React for UI updates (Virtual DOM). Angular is highly performant, especially for complex apps, with recent speed improvements. Performance depends on the use case
When to choose React & Angular?
React: Flexible projects, dynamic UIs, SPAs, mobile (React Native), faster start. Angular: Large/enterprise apps, structure needed, all-in-one solution preferred.
Which is more popular in 2025?
React leads in developer surveys, community size, and job postings. Angular remains very popular, especially in enterprises.
Easier to learn?
Generally React (JavaScript focus). Angular has a steeper curve (TypeScript, full framework concepts).
Who uses them?
Angular: Google, PayPal, Samsung, Nike. React: Meta (Facebook/Instagram), Netflix, Airbnb, Walmart.