Quick Summary :- These operating models have a big impact on how global teams are built, run and kept on track. Here's a quick rundown of the key points: how the governance structure works, the operating choices you've got and why having a clear plan in place is so vital when you're making those tough ownership decisions and responsibilities are increasing fast.
With critical work being done by Global Capability Centers, businesses can’t afford to have systems and processes down for a second. This has turned the way we look at their role on its head and where responsibility really rests. But what happens when we start to question who’s really in charge?
As responsibilities grow, structure becomes more than an early setup decision. The operating model shapes how a GCC starts how control is shared and how responsibility develops. In the case of governance, there will be issues regarding who makes decisions, what types of issues can be raised and how to assess performance.
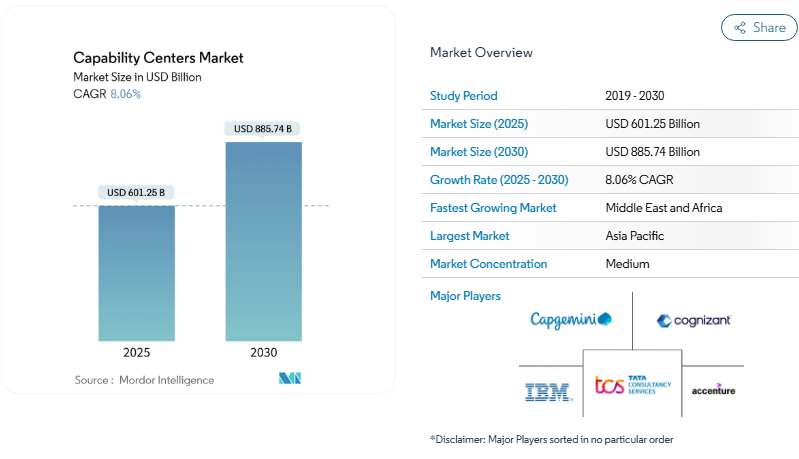
The purpose of Commercial Match Matters is to develop a method for valuing products based on their value to customers and not by the effort it takes to produce the products. The Global Capability Centers market valued at 885.74 billion by 2030, Build Operate Transfer and related business models will provide future benchmarks for balancing immediate implementation with long term control.
What Is a GCC Operating Model?
An operating model defines how a Global Capability Center is organized, governed, funded and developed shaping ownership control cost outcomes.
- Decides who owns the center and the decision authority
- Sets responsibility across delivery governance and direction
- Defines how operational and alignment risks are shared
- Builds visibility into ongoing cost responsibilities
- Guides location strategy based on workforce availability and capability
- Nearly 70% of companies opt to set up GCC in India and Eastern Europe due to ongoing access to skilled talent pools
Why GCC Operating Model Choice Impacts Long-Term Outcomes?
The chosen operating model affects how costs are controlled and responsibility is improved over time, shaping outcomes that are difficult to reverse later.
- Decides whether cost growth follows clear planning or appears through gradual shift in operations
- Affects how consistently day to day operations continue during leadership changes or workload shifts
- Implements how clearly decisions approvals and growth are understood across the center
- Shapes where financial, legal and delivery risks sit when priorities change or issues come up
- Leads whether experienced team members remain engaged or cycle out during shifts
- Guides how easily the center adjusts its role as business priorities and expectations change
- Build Operate Transfer(BOT) models are estimated to grow at a 9.23% CAGR through 2030, showing choice for planned shifts and managed clarity
🤔 Did you know?
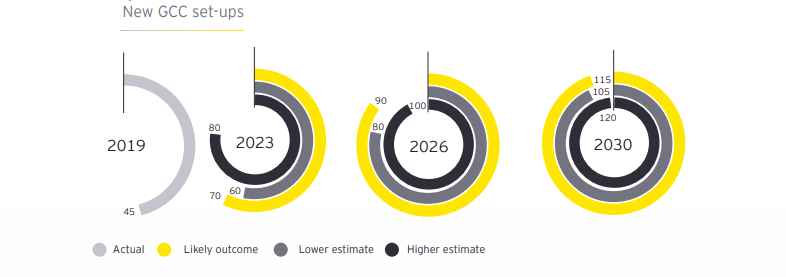
By 2030, new GCC set-ups are expected to surge, with a likely 115 centers and a realistic band of 105 to 120 globally.
Which GCC Operating Models Organizations Commonly Use?
Organizations adopt different GCC operating models based on control risk margin and long-term intent. Each model reflects how ownership responsibility and operational involvement are expected to grow over time.
1. Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT) Model
The Build Operate Transfer model starts with partner-led setup and operations, then slowly hands control to the organization after processes teams and governance mature.
What This Model Delivers
- Faster center launch without early operational challenge
- Reduced setup risk through experienced local execution
- Planned transfer path into internal management
- Early access to built hiring and developed systems
What Needs Early Planning
- Clear transfer milestones and decision checkpoints
- Ownership terms for assets contracts and knowledge
- Governance rules during shared operating phase
- Internal readiness for post transfer management
Where This Model Fits Best
BOT model suits organizations entering new regions where local expertise is limited and early execution speed matters more than immediate control while future independence remains a clear objective.
🏭Industry context: BOT-based GCCs increased from under 10% to nearly 40% of setups and increased to 90% when assisted transfer approaches are included.
2. Captive GCC Model
The captive model places full ownership operations and decision authority directly with the organization from day one without third-party operational involvement.
Key Advantages
- Full Control on Strategy Budgets and Execution
- Strong Alignment to Internal Culture and Business Priorities
- Full ownership of intellectual property and data
- Supported by a USD 1.1 billion captive GCC portal market, indicating sustained enterprise investment
Points to Watch
- Higher Upfront Investment in Initial Set Up
- Slower Time to Market without Local Execution Partners
- Increased Compliance and Administrative Responsibility
- Leadership Capacity Required for Daily Supervision
Best Fit For
The captive model works best for organizations with established global operations, strong internal governance and readiness to manage hiring, compliance and operational responsibility independently from the outset.
3. Managed Services Model
The managed services model places day-to-day GCC operations with a provider while the organization retains oversight through defined performance and governance controls.
Operational responsibilities usually managed externally
- Daily staffing and operational workflows for delivery execution
- Implementing infrastructure support, managing security and developing continuity planning
- Handling compliance through reporting and monitoring service performance
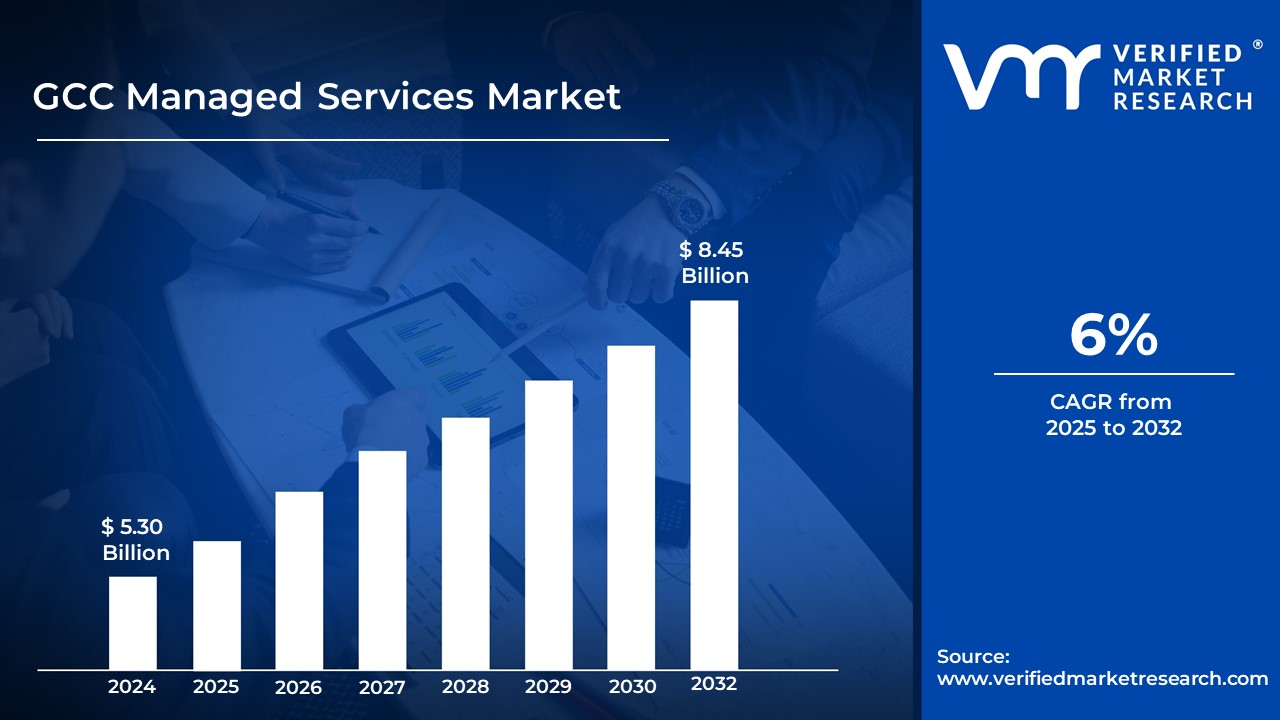
- The market is expected to be valued at USD 8.45 billion by 2032, as organisations increasingly depend on these types of solutions.
Reasons enterprises adopt this approach
- Reducing the number of routine operational tasks it performs internally.
- Increasing the speed of setup and providing an established set of assets with which to deliver services.
- Providing a clear line of responsibility for service delivery, resulting in a measurable outcome.
- Reducing reliance on the organisation’s internal management bandwidth for oversight of operations
Most Effective When
This model works best when organizations want consistent outcomes without building internal operating depth, allowing leadership to concentrate on governance priorities, strategic direction and business performance.
Also Read: Managed GCC vs Captive GCC: Which Model Fits Your Enterprise?
4. Hybrid GCC Operating Model
The hybrid model combines internal ownership with selective partner involvement, allowing shared responsibility across setup operations and gradual capability consolidation.
Core strengths delivered through this structure
- Balance between internal control and external execution support
- Gradual capability development without full operational exposure
- Shared accountability across critical operational functions
- Adoption growth reflected by a USD 227.0 billion market projection by 2032, driven by mixed ownership demand
Areas requiring deliberate coordination
- Clear boundaries between internal teams and partners
- Defined decision ownership during shared responsibility phases
- Alignment on performance expectations and reporting cadence
- Strong governance to prevent role overlap or gaps
Where This Model Works Best
The hybrid approach suits organizations seeking control over critical functions while relying on partners for specific capabilities during transition periods without committing fully to one operating structure.
5. Joint Venture GCC Model
The joint venture model shares ownership and governance between the organization and the partner, combining investment risk decision authority and operational responsibility.
Shared value outcomes
- Shared capital commitment reduces individual investment exposure
- Joint oversight improves automation-driven efficiency gains
- Cost savings near 20% achieved through consolidation
- Processes improve up to 35% via coordinated automation
Critical considerations before forming
- Clear equity structure and profit-sharing rules
- Aligned objectives across both governing parties early
- Defined exit terms to avoid future disputes
- Integrated governance model covering compliance decisions jointly
Where This Model Applies Best
This model fits organizations seeking shared investment and influence where market entry requires local participation and automation benefits justify joint decision making complexity over time.
📈 GCC Growth Anchor
India is currently the world’s fifth-largest economy and is expected to rank third by 2030, which explains its growing importance in global GCC strategy decisions.
How GCC Governance Models Control Decisions, Accountability and Risk?
Governance models define how authority management and responsibility operate within a GCC providing control without slowing execution or day to day progress.
- Clarifies who holds final decision authority across critical functions
- Controls budget ownership and hiring approvals across operating cycles
- Measures performance against agreed outcomes not activity volume
- Make sure legally required and agreed duties are consistently carried out
- Protects intellectual property and sensitive data across jurisdictions
- Nearly 50 percent of new-age enterprise skills are built within GCCs, requiring clear elevation paths and ownership discipline
Comparing GCC Operating Models by Business Priority
Most organizations compare GCC models based on control risk handling and transition clarity rather than evaluating every structure independently.
Simplified Comparison With Model Examples
| Business Priority | How It Commonly Shows Up | Example Models |
| Speed of initial setup | Partner involvement shortens early timelines, while internally built centers take longer to stabilize | BOT, Managed Services |
| Control and decision authority | Direct ownership keeps authority internal, while shared structures require negotiated control | Captive, Joint Venture |
| Risk responsibility | Some models absorb early delivery risk externally others place responsibility fully inside | BOT, Managed Services vs Captive |
| Transition and exit clarity | Defined handover paths reduce uncertainty compared to equity or contract unwind | BOT, Hybrid |
| Operational focus | Outcome delivery differs from ownership-driven execution depending on the structure | Managed Services vs Captive |
How to Select the Right GCC Operating Model?
Selecting the right GCC operating model depends on making decisions in a clear sequence so that structure governance and accountability align with operating realities.
- Step 1: Review business maturity by examining prior global delivery experience, leadership capacity and ability to manage distributed teams.
- Step 2: Establish risk tolerance by identifying acceptable exposure across GCC legal compliance, operations and delivery during early and transition stages.
- Step 3: Validate compliance requirements, including data protection labor regulations and industry rules that influence ownership and operating choices.
- Step 4: Assess internal governance readiness by confirming decision rights escalation paths, performance oversight and accountability discipline.
- Step 5: Define ownership direction by deciding whether partner involvement is temporary or expected to continue over time.
- Step 6: Ensure outcome measurement capability by confirming systems exist to track delivery quality cost behavior and responsibility consistently.
Which GCC Operating Model Is Preferred by eSparkBiz?
Across GCC engagements, eSparkBiz supports multiple operating approaches, with Build-Operate-Transfer commonly preferred where controlled setup and phased responsibility are required.
- Commercial terms are aligned to defined delivery outcomes, with pricing reviewed against verified results rather than time-based effort
- BOT is typically selected when early execution must mature into an internal control supported by governance checkpoints
- GCC Setup Pricing milestones follow responsibility handover stages to maintain balance during transition
- Governance frameworks validate performance data before any commercial adjustment
- In one GCC engagement, eSparkBiz applied a BOT-led structure with upfront planning to support a structured and controlled transition
- AWS-certified teams support cloud-based GCC environments
- ISO-certified delivery and security processes reinforce governance expectations
- Maintains consistent 5-star ratings on the HubSpot platform, reflecting transparency and delivery discipline
Conclusion
Strong alignment between operating structure and governance determines whether a GCC delivers sustained capability or ongoing operational strain. Model selection influences decision authority, risk placement, cost behavior and accountability patterns that continue shaping outcomes well beyond initial setup.
Build Operate Transfer stands out as a practical starting point when early execution speed must coexist with future internal control. When combined with value-based pricing and disciplined governance, BOT supports structured progression, informed decisions and outcome accountability rather than short-term delivery focus.
Collaborate with eSparkBiz to choose the ideal GCC operating model for long-term business outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a GCC operating model?
A GCC operating model defines ownership governance risk allocation and responsibilities shaping how offshore capabilities are built managed and transitioned.
When is the BOT model typically appropriate?
BOT suits organizations seeking fast GCC setup timeline with reduced early risk while retaining a clear path toward internal ownership control.
Why is governance critical in GCC structures?
Governance ensures decisions budgets performance oversight and compliance remain controlled preventing accountability gaps as GCC responsibilities expand over time globally.
What does value-based pricing mean in GCC engagements?
Value-based pricing links commercial terms to measured outcomes aligning tax incentives, governance discipline and delivery responsibility across GCC engagements consistently effectively.
How should organizations choose the right GCC model?
Selecting a GCC model requires evaluating maturity, risk tolerance, compliance readiness, governance strength and clarity on future ownership intent objectives.