Quick Summary :- To get the right NodeJS developer, one has to ask the right questions. This guide defines essential competency areas and Node.JS Interview Questions to test a candidate’s real skills – from fundamentals to real-world scenarios. For both fresher and experienced candidates, the Node.JS interview questions include basics, APIs, databases, problems, security, and many others.
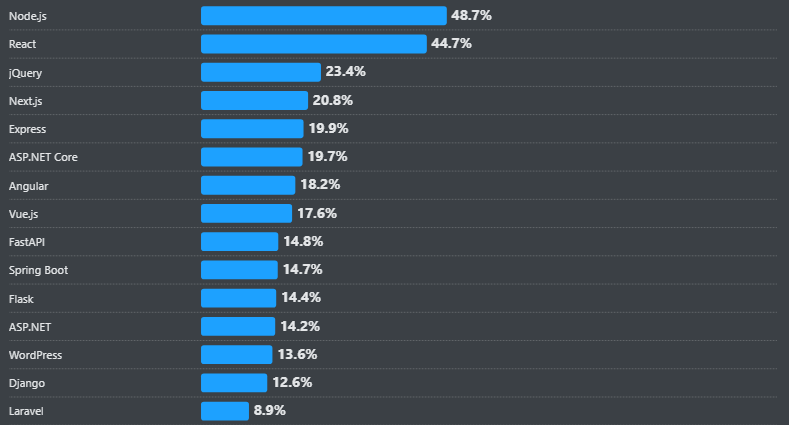
NodeJS emerged in the tech landscape as a powerful JavaScript framework for building lightning-fast, scalable server-side applications. Its popularity continues to rise, with around 48.7% of experienced web developers using Node.js frameworks, libraries, IDEs, and tools for their web application projects. As companies race to deliver robust digital products, skilled NodeJS talent has become more critical than ever.
However, one thing remains clear—you can’t use the same Node.js interview questions for every candidate. Whether you’re evaluating a junior developer or a seasoned senior engineer, your interview strategy must align with their experience level and real-world expertise.
This guide helps you conduct effective NodeJS interviews. We’ve handpicked essential Node.js interview questions and answers that deeply assess a candidate’s skills, ensuring you hire the ideal professional for your team.
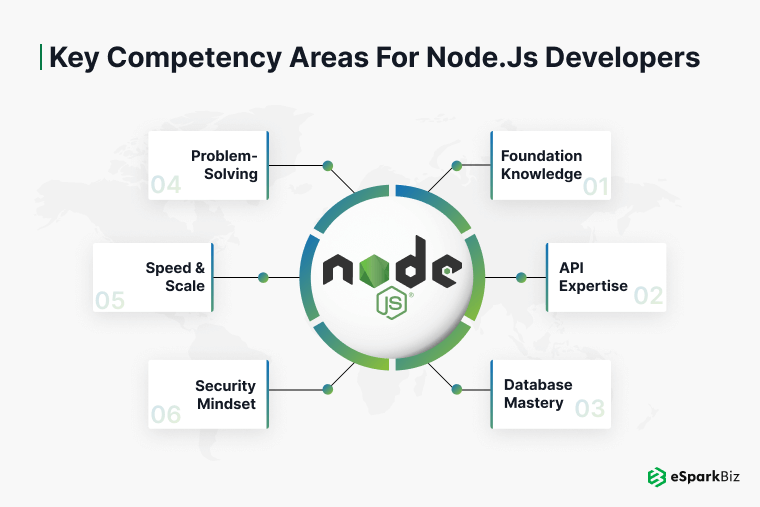
Essential Skills to Look for in a Node.js Developer
These core competency areas help evaluate a Node.js developer’s real-world expertise, from fundamentals and APIs to performance optimization and application security.
When evaluating candidates, focus on these crucial areas:-
- Foundation Knowledge: Do they know how to navigate NodeJS Development core concepts and handle the asynchronous code like a pro?
- API Expertise: Look at how they can craft and maintain strong REST services
- Database Mastery: Test them on their SQL and NoSQL database handling
- Problem-Solving: Review how they approach bugs and handle error cases
- Speed & Scale: See how well they execute code fast and efficiently
- Security Mindset: Make sure that they fully understand Node’s security fundamentals
Top Node.js Interview Questions based on Experience Level
Junior-Level Node.js Developer Questions
These questions evaluate a candidate’s understanding of Node.js fundamentals, asynchronous programming, and basic backend concepts.
Q1: What is Node.js and why is it beneficial to use it?
Expected Answer:
Node.js is a cross-platform, open-source JavaScript runtime environment built on Google’s V8 JavaScript engine. It allows developers to run JavaScript code outside the browser, mainly on the server side.
Node.js follows a non-blocking, event-driven architecture, which enables it to handle multiple requests efficiently. This makes it a strong choice for building fast, scalable applications such as APIs, real-time apps, and streaming platforms.
One of the major benefits of Node.js is that it allows developers to use JavaScript for both frontend and backend, ensuring code consistency and faster development.
Key Elements in Their Answer:
- They should clearly explain what Node.js is and its primary use case.
- Look for references to Google’s V8 JavaScript engine, which plays a key role in performance.
- They should demonstrate an understanding of asynchronous and non-blocking operations, which is a key benefit of Node.js.
- They should mention why Node.js is suitable for scalable and I/O-heavy applications.
Dig Deeper With:
- “Can you share an example where Node.js was a better choice than other backend technologies or frontend frameworks?”
- “How would you describe the single-threaded nature of Node.js and how it handles concurrency?”
Watch Out For:
- Unclear understanding of asynchronous operations, which is a core Node.js concept.
- Inability to provide real-world examples may indicate limited practical experience.
Q2: What is npm and what is its role in Node.js programming?
Expected Answer:
npm (Node Package Manager) is the default package manager for Node.js. It is used to install, manage, and update third-party libraries and dependencies required in a Node.js application.
npm provides access to a large ecosystem of open-source packages, helping developers build applications faster without writing everything from scratch. It also helps manage project configurations through files like package.json, which define dependencies, scripts, and versioning.
Key Elements in Their Answer:
- They should explain that npm stands for Node Package Manager and it is one of the popular NodeJS packages.
- They should understand how npm is used to install, update, and manage dependencies.
- Look for familiarity with common npm commands such as npm install, npm update, and npm uninstall.
- They should recognize the role of package.json in managing project dependencies and scripts.
Dig Deeper With:
- “How will you manage packages and update them to the latest NodeJS version with npm?”
- “What is the purpose of the package.json file in your projects?”
Watch Out For:
- Struggling with basic npm commands may indicate limited hands-on experience.
- Confusion around package.json suggests a need for more practical exposure.
Mastering package.json: A Comprehensive Guide 🚀 #nodejs #javascript #webdev #dormosheio #softwaredevelopment #softwareengineering #programming #frontenddev https://t.co/n0gwfhUrdv
— NodeJS Trends (@NodejsTrends) November 18, 2024
Q3: How does synchronous and asynchronous programming work in Node.js?
Expected Answer: Consider sync programming as a line at a coffee shop where one order has to be done before the next one begins. Async programming is a concept that is quite similar to a restaurant where multiple orders are being prepared at the same time.
Similarly, Node JS manages this through the callback function, promise, and through the use of the await and several asynchronous function calls.
Key Elements in Their Answer:
- Good understanding of the concept of blocking and non-blocking code flows that helps to assure consistent code style.
- Knowledge of Node.js functions (callback functions, promises, utility functions, asynchronous programming with asynchronous functions & await).
- Why async is important for app performance
Dig Deeper With:
- ”Describe an example where the use of async programming in Node.js was beneficial.”
- “What strategies have you used to manage errors in async code, particularly with the callback function?”
Watch Out For:
- If they cannot distinguish between synchronous and asynchronous operations that is a common skill deficit.
- A lack of understanding of how to handle errors in the asynchronous flows can lead to problems later on.
Q4: Can you explain how an event loop works in the context of Node.js?
Expected Answer:
The event loop is a core part of Node.js that allows it to handle asynchronous, non-blocking operations efficiently. It continuously checks the call stack and processes tasks from different queues once the stack is empty.
When an asynchronous operation (like a timer, API call, or file read) is completed, its callback is placed in the appropriate queue. The event loop then pushes these callbacks to the call stack for execution, ensuring the application remains responsive while handling multiple requests.
Key Elements in Their Answer:
- Understanding of non-blocking I/O in Node.js.
- Ability to explain the relationship between the call stack, event loop, and task/callback queues.
- Explanation of why the event loop is critical for handling concurrent requests in a single-threaded environment.
Dig Deeper With:
- “What role does the call stack play in the event loop?”
- “How does the event loop manage asynchronous operations in Node.js?”
Watch Out For:
- Misunderstanding the event loop often indicates weak Node.js fundamentals.
- Inability to explain task or callback management may suggest limited practical experience.
Mid-Level Node.js Developer Questions
These questions assess hands-on experience with APIs, middleware, error handling, and performance optimization in real-world Node.js applications.
Q5: Explain the difference between require and import in Node.js.
Expected Answer:
require is part of the CommonJS module system, which has traditionally been used in Node.js to load modules synchronously at runtime. It is commonly used in older Node.js projects and does not require special configuration.
import is part of the ES Modules (ESM) specification introduced in ES6. It allows modules to be loaded in a more structured and standardized way. While import statements are statically analyzed, Node.js supports them when ES modules are enabled using the .mjs extension or by setting “type”: “module” in package.json.
Node.js supports both module systems, and developers should choose based on project requirements, compatibility, and modern JavaScript standards.
Key Elements in Their Answer:
- Clear understanding that require belongs to CommonJS and import belongs to ES Modules (ES6).
- Awareness that require is evaluated synchronously, while import is statically resolved.
- Ability to explain when and why one should be used over the other.
- Knowledge of how Node.js supports both module systems.
Dig Deeper With:
- “Why would you choose import over require in a modern Node.js application?”
- “How do you configure Node.js to use ES Modules?”
Watch Out For:
- Lack of understanding of Node.js module systems indicates a fundamental knowledge gap.
- Confusion around compatibility or configuration may cause issues in real-world projects.
Q6: What are middleware functions in Express.js, and how are they used?
Expected Answer:
Middleware functions in Express.js are functions that have access to the request (req), response (res), and the next (next) function in the application’s request–response cycle. They are executed sequentially and can modify the request or response, perform logic, or end the request cycle.
Middleware is commonly used for tasks such as authentication, logging, request validation, error handling, and parsing request data before the request reaches the final route handler.
Key Elements in Their Answer:
- Understanding of how middleware fits into the Express request–response lifecycle.
- Ability to explain how middleware can modify requests or responses or control flow using next().
- Real-world examples such as authentication, logging, or input validation.
- Knowledge of how multiple middleware functions can be combined and executed in layers.
Dig Deeper With:
- “How would you implement authentication using middleware in Express.js?”
- “Can middleware functions be asynchronous, and how does Express handle them?”
Watch Out For:
- Inability to provide practical use cases for middleware.
- Confusion about middleware flow and execution order, which is a core Express.js concept.
Q7: Explain how you would approach error management in a Node.js application.
Expected Answer:
Error management in a Node.js application involves handling both synchronous and asynchronous errors in a consistent and structured way. Synchronous errors are typically handled using try/catch blocks, while asynchronous errors are managed using promise .catch() handlers or async/await with try/catch.
In Express.js applications, errors are often handled using a centralized error-handling middleware, which ensures consistent error responses and easier debugging. Additionally, Node.js provides global error handlers such as process.on(‘uncaughtException’) and process.on(‘unhandledRejection’) as a last-resort safety mechanism.
Key Elements in Their Answer:
- Strong understanding of asynchronous error handling using promises and async/await.
- Knowledge of centralized error-handling middleware in Express.js.
- Awareness of Node.js global error handlers and when they should be used.
- Understanding the importance of logging errors for debugging and monitoring.
Dig Deeper With:
- “Why is centralized error handling important in Express.js applications?”
- “How do you monitor and track errors in a live Node.js application?”
Watch Out For:
- Confusion around handling errors in asynchronous code may cause issues in advanced Node.js development.
- Lack of awareness of global error handlers may indicate limited real-world experience.
Q8: What is clustering in Node.js, and when would you use it?
Expected Answer:
Clustering in Node.js is a technique that allows an application to utilize multiple CPU cores by creating multiple worker processes. Since Node.js runs on a single thread by default, the cluster module helps improve performance by spawning child processes that share the same server port.
Clustering is commonly used in high-traffic or CPU-intensive applications where handling a large number of concurrent requests efficiently is required. It helps improve scalability, reliability, and overall application throughput.
Key Elements in Their Answer:
- Clear understanding of clustering as a solution for multi-core CPU utilization.
- Knowledge of how the Node.js cluster module creates and manages worker processes.
- Ability to explain when clustering is beneficial, especially in high-concurrency scenarios.
Dig Deeper With:
- “What is the difference between clustering and load balancing?”
- “What are some drawbacks or challenges of using the Node.js cluster module?”
Watch Out For:
- Uncertainty about why clustering is important for performance and scalability.
- Lack of familiarity with the Node.js cluster module, which may indicate limited real-world experience.
Q9:How does Node.js handle file I/O, and what are the common Node.js methods for reading and writing files?
Expected Answer:
Node.js handles file I/O using the built-in File System (fs) module, which provides both synchronous and asynchronous methods for interacting with the file system. For basic file operations, asynchronous methods such as fs.readFile() and fs.writeFile() are commonly used.
When working with large files, Node.js supports streams, such as fs.createReadStream() and fs.createWriteStream(), which allow data to be processed in chunks instead of loading the entire file into memory. Synchronous file methods should be used cautiously, as they can block the event loop and impact application performance.
Key Elements in Their Answer:
- Understanding of the fs module and its synchronous and asynchronous methods.
- Knowledge of using streams for handling large files efficiently.
- Awareness of performance issues caused by blocking synchronous file I/O.
Dig Deeper With:
- “What is the difference between fs.readFile() and fs.createReadStream()?”
- “How do you handle errors in asynchronous file system operations?”
Watch Out For:
- Lack of understanding of streams may cause performance issues when handling large files.
- Confusion between synchronous and asynchronous file I/O can negatively impact scalability.
Senior Node.js Developer Questions
These questions focus on system design, scalability, concurrency management, security, and production-grade Node.js architecture.
Q10: How would you design a scalable Node.js application architecture?
Expected Answer:
Designing a scalable, enterprise-level NodeJS application Node.js application starts with a modular architecture that separates concerns and allows independent scaling. Depending on the use case, this may involve choosing between a monolithic, microservices, or serverless architecture.
Scalability is achieved by using techniques such as clustering to leverage multi-core CPUs, load balancing to distribute traffic, and horizontal scaling in cloud environments. Performance optimization strategies like caching, message queues, and API gateways are commonly used to handle high traffic and improve reliability.
Key Elements in Their Answer:
- Ability to decide when to use monolithic vs microservices architectures.
- Understanding of clustering, load balancing, and serverless approaches for scaling Node.js applications.
- Knowledge of integrating caching, queuing systems, and API gateways to enhance performance and resilience.
- Awareness of cloud-based scaling strategies.
Dig Deeper With:
- “What are the pros and cons of using a microservices architecture?”
- “What architecture would you recommend for deploying a Node.js application in the cloud, and why?”
Watch Out For:
- Lack of familiarity with common scalability and architectural patterns.
- Failure to discuss clustering, load balancing, or serverless options may indicate limited system-design experience.
Q11: How do you monitor and optimize the performance of a Node.js application in production?
Expected Answer:
Monitoring and optimizing a Node.js application in production requires a combination of real-time monitoring, logging, profiling, and performance testing. Tools such as New Relic, Datadog, Prometheus, and the ELK stack are commonly used to track system metrics, application performance, logs, and errors.
For optimization, developers use strategies like caching, efficient database queries, memory and CPU profiling, connection pooling, and code optimization. Additionally, test-driven development are essential to identify bottlenecks and ensure the application performs reliably under heavy traffic.
Key Elements in Their Answer:
- Awareness of production monitoring and observability tools such as New Relic, Datadog, Prometheus, or ELK.
- Familiarity with performance optimization techniques including caching, profiling, and query optimization.
- Understanding the importance of load and stress testing for performance tuning.
- Knowledge of monitoring CPU usage, memory consumption, and event loop latency.
Dig Deeper With:
- “Which tools have you personally used to monitor Node.js applications in production?”
- “How do you detect and resolve memory leaks in a Node.js application?”
Watch Out For:
- Lack of hands-on experience with real-time production monitoring tools.
- Failure to explain the importance of load testing may indicate limited production exposure.
Q12: How does Node.js handle concurrency, and how would you manage high-load scenarios?
Expected Answer:
Node.js handles concurrency using a single-threaded event loop combined with asynchronous, non-blocking I/O. This allows it to manage multiple client requests efficiently without creating multiple threads for each request. While this model works well for I/O-bound tasks, CPU-intensive operations can block the event loop and degrade performance.
To handle high-load scenarios, developers can use clustering to spawn multiple Node.js processes across CPU cores, leverage worker threads for computationally heavy tasks, or offload processing to external services or queues. These strategies ensure that the application remains responsive even under heavy traffic.
Key Elements in Their Answer:
- Understanding of the event loop and asynchronous I/O for concurrency.
- Awareness of clustering and worker threads to scale Node.js applications.
- Ability to delegate CPU-intensive tasks to maintain responsiveness.
- Knowledge of practical strategies for managing high-load scenarios.
Dig Deeper With:
- “How does the single-threaded model of Node.js impact concurrency in real applications?”
- “When would you prefer using worker threads over the cluster module?”
Watch Out For:
- Lack of understanding of concurrency management in Node.js.
- Failure to discuss worker threads, clustering, or offloading may indicate limited experience with high-load applications.
Q13: What is the role of process.nextTick() and setImmediate() in Node.js, and how do they differ?
Expected Answer:
process.nextTick() and setImmediate() are functions that allow developers to schedule callbacks in the Node.js event loop with different priorities.
- process.nextTick() executes a callback immediately after the current operation completes, before the event loop continues to the next phase.
- setImmediate() schedules a callback to run in the next iteration of the event loop, after I/O events and timers in the current cycle have been processed.
These functions give developers control over execution order, timing, and prioritization of asynchronous tasks within the event loop.
Key Elements in Their Answer:
- Knowledge of event loop phases and how nextTick and setImmediate fit in.
- Ability to provide practical examples of when each function should be used.
- Clear comparison of timing and priority between process.nextTick() and setImmediate().
Dig Deeper With:
- “When would you choose process.nextTick() over setImmediate()?”
- “How does setTimeout() relate to process.nextTick() and setImmediate() in terms of event loop execution order?”
Watch Out For:
- Uncertainty about event loop timing and the purpose of these scheduling functions.
- Lack of real-world examples demonstrating practical use.
Q14: Describe how you would implement secure coding practices in a Node.js application.
Expected Answer:
To develop a secure Node.js application, developers should store sensitive information such as API keys, database credentials, and secrets in environment variables or secure vaults. All user inputs should be validated and sanitized to protect against SQL injection, command injection, and XSS attacks.
Authentication and authorization should be handled securely using JWT tokens, OAuth, or other reliable methods. All communication should use HTTPS, and security headers such as CSP and CORS should be properly configured to prevent attacks.
Additionally, applications should be regularly monitored and audited, dependencies kept up to date, and logging implemented to detect suspicious activity. Following these practices helps ensure that Node.js applications remain robust against common security threats.
Key Elements in Their Answer:
- Awareness of secure storage of sensitive data.
- Understanding of input validation and sanitization to prevent attacks.
- Knowledge of secure authentication methods and HTTPS usage.
- Familiarity with security headers (CSP, CORS) and monitoring.
Dig Deeper With:
- “If you are developing a Node.js MVC application, how would you prevent SQL injection?”
- “Which tools or libraries would you use to perform security scanning in Node.js?”
Watch Out For:
- No mention of secure storage of credentials.
- Limited understanding of common threats and countermeasures.
- Lack of knowledge regarding secure communication and headers.
Q15: Explain how you would implement a rate limiter in Node.js API functions to prevent abuse.
Expected Answer:
Rate limiting is a strategy used to control the number of requests a client can make to an API within a specific timeframe, protecting against abuse and reducing server load. In Node.js, this can be implemented using libraries such as express-rate-limit for single-server setups or Redis for distributed rate limiting across multiple instances.
Rate limiting is particularly important for public-facing APIs, login endpoints, and other sensitive routes. It ensures fair usage, prevents denial-of-service attacks, and helps maintain overall system stability under high traffic conditions.
Key Elements in Their Answer:
- Awareness of rate limiting as both a security and performance mechanism.
- Knowledge of tools and libraries such as express-rate-limit and Redis for implementing rate limiting.
- Understanding when and where to apply rate limiting, such as for public APIs or high-risk endpoints.
- Awareness of distributed rate limiting strategies for multi-instance or clustered applications.
Dig Deeper With:
- “How do you implement rate limiting in a clustered or distributed Node.js environment?”
- “Why is Redis commonly used for distributed rate limiting?”
Watch Out For:
- Lack of knowledge about rate-limiting libraries or tools.
- No discussion of distributed rate-limiting strategies, which may indicate limited experience in production-grade API development.
Why Hire Node.js Developers from eSparkBiz?
Want to develop the next big hit using NodeJS? Hire NodeJS Developers at eSparkBiz to achieve your dream NodeJS results. Our team of NodeJS developers consists of experienced professionals with 15+ years of work experience and CMMI Level 3 certification. From a new team member to address basic tasks to a professional with experience in designing a robust system, our developers will deliver. Here’s how we can help at every experience level:
Junior NodeJS Developers
Our junior developers – eager beavers ready to make an impact – are proficient in NodeJS fundamentals and REST API development. They will with those fundamental components with vigor so that your project is off to a strong beginning.
Mid-Level NodeJS Developers
Our mid-level crew, seasoned problem-solvers, know how to connect strategy with proper Javascript code execution. NodeJS best practices for API integration, error handling, performance optimization – they’ve got the practical knowledge to make your application smooth as silk.
Senior NodeJS Developers
Our senior developers are the architects and security experts who know how to build secure, fault-tolerant applications. Whether it is setting up a top-notch architecture with microservices best practices or strengthening performance, they are fully equipped to handle your most complex issues.
Offering both fixed and hourly pricing models and listening closely to the needs of our clients, eSparkBiz is your go-to solution for NodeJS. So why settle for less? Choose the best and see your application fly to greater heights. Consult with NodeJS Experts at eSparkBiz Today!
Conclusion
To build high-performance and scalable applications, hiring the right NodeJS developer skills. is essential. Interview questions should be tailored to the candidate’s experience level to accurately assess their understanding of core concepts, Node.js architecture, and real-world development practices.
By focusing on NodeJS fundamentals such as event loops, concurrency, security, and scalability, these targeted interview questions help you identify professionals with both technical expertise and practical problem-solving skills.
Frequently Asked Questions
What core Node.js skills should I assess during an interview?
Evaluate a candidate’s knowledge of asynchronous programming, event driven architecture, error handling and modular coding. Practical experience with REST API integration, database operations and application performance management indicates enterprise level readiness.
Which Node.js frameworks or libraries should candidates know?
Candidates should be familiar with web frameworks such as Express.js, Koa or Fastify, along with ORMs like Sequelize or Mongoose. Experience with testing tools, including Jest or Mocha, demonstrates production grade development skills.
How can I test a candidate’s knowledge of asynchronous patterns?
Ask scenario based questions involving callbacks, promises and async/await. Assessing their understanding of event loops, concurrency handling and non-blocking operations reveals ability to build responsive, maintainable and high performance Node.js applications.
Which questions reveal a candidate’s approach to performance optimization?
Probe techniques for memory management, caching strategies, event loop monitoring and clustering. Candidates should explain profiling methods, identifying bottlenecks and improving response times for applications under high traffic or data intensive workloads.
How do I assess a candidate’s knowledge of Node.js security best practices?
Evaluate understanding of input validation, authentication, encryption and dependency management. Experience preventing common vulnerabilities, including injection attacks and data leaks, demonstrates capability to maintain secure, enterprise grade Node.js applications.